Kivy Widget: Label, Button
Subject: Mobile Application Development (VU-CSS 223)A widget in Kivy is any graphical element used to build the user interface (UI), such as buttons, labels, text boxes, and layouts.
Label Widget
Used for displaying static text.
from kivy.uix.label import Label Label(text="Welcome to Kivy")
Common Properties
- text
- font_size
- color
These properties are used across many Kivy widgets such as Label, Button, and TextInput to control how text appears on the screen.
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.label import Label class MyApp(App): def build(self): return Label(text="Welcome to my app") MyApp().run()
Explanation
1. from kivy… Importing Required Classes
- App is the main application class in Kivy.
- widget you want user to use e.g Label, Button etc
2. class MyApp(App) Creating the App Class
- This defines your application.
- It inherits from App, which gives it Kivy functionality.
3. def build(self) The build() Method
- This method builds and returns the user interface (UI)
- Kivy automatically calls it when the app starts.
4. Label(text="Welcome to my app") Create a widget e.g Lable, Button
5. return... Displays the widget e.g label, button as the main UI of the app
6. MyApp().run() Starts and runs the Kivy application
Example with size
lbl = Label(text="Welcome to my app", font_size=30) return lbl
Example with color
(Red, Green, Blue, Alpha)
Label(text="Red Text", color=(1, 0, 0, 1)) Label(text="Blue Text", color=(0, 0, 1, 1))
Button Widget
Used for user interaction.
from kivy.uix.button import Button
btn = Button(text="Click Me")
Event Handling
btn.bind(on_press… something happens)
Full Code
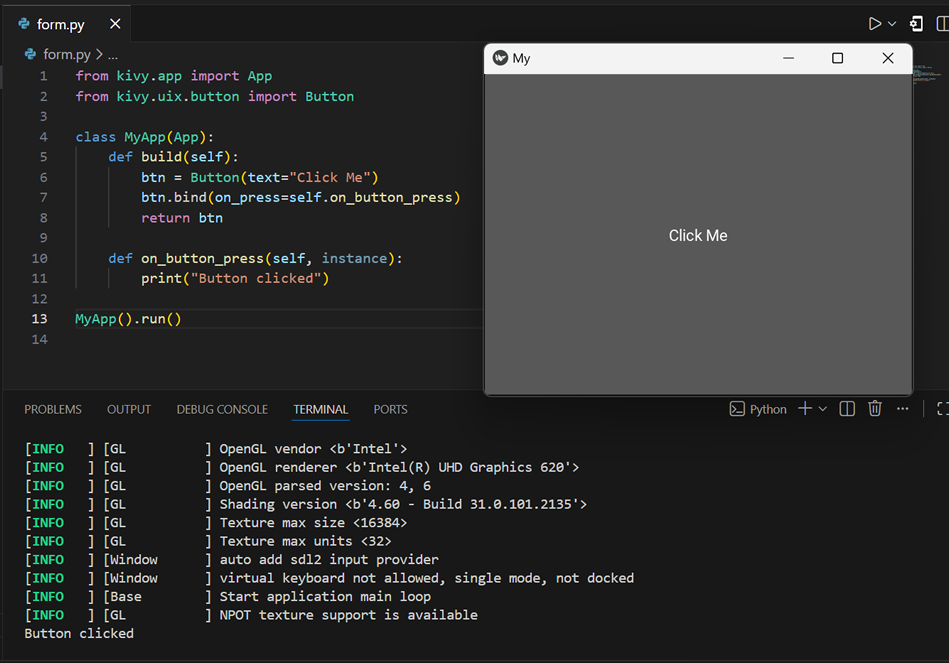
from kivy.app import App from kivy.uix.button import Button class MyApp(App): def build(self): btn = Button(text="Click Me") btn.bind(on_press=self.on_button_press) return btn def on_button_press(self, instance): print("Button clicked") MyApp().run()
Explanation
1. btn.bind(on_press=self.on_button_press) Binding the Button to an Event
- This connects the button’s click event to a function.
- When the button is pressed, on_button_press() is called.
2. def on_button_press(self, instance): Handling the Button Click
- This function runs when the button is clicked.
- instance represents the button that was clicked.
- It prints Button clicked in the terminal.
By: Vision University
Comments
No Comment yet!
Login to comment or ask question on this topic
Previous Topic Next Topic
- 1 Introduction to Mobile Application Development
- 2 Understanding the Kivy Framework
- 3 Kivy Widget: Label, Button
- 4 Kivy Screens, Navigation & State Management