Introduction to API
Subject: Microservice Programming (VU-CSS 325)API stands for Application Programming Interface. It’s a set of rules and protocols that allows one software application to communicate with another. Think of it as a messenger: you send a request, the API delivers it to the system, and then brings back the response.
Attributes of an API
1. Request & Response: a client (like a browser or mobile app) sends a request and the server processes it and sends back a response (usually in JSON or XML).
2. Endpoints: are specific URLs that represent resources. For example: GET /users to fetch all users.
3. HTTP Methods: are used to indicate the action an API client would like to perform on a given resource. For example:
◦ GET: Retrieve data
◦ POST: Create new data
◦ PUT/PATCH: Update existing data
◦ DELETE: Remove data
4. API Response: an API response is the data sent back from the server after it processes a client’s request. It usually contains:
◦ Status code: tells whether the request succeeded or failed.
◦ Headers: metadata (like content type, length, etc.).
◦ Body: the actual data (often JSON).
5. Data Format: most modern APIs use JSON because it’s lightweight and human-readable.
Common HTTP Status Codes
- 200 OK: Request succeeded.
- 201 Created: New resource created.
- 400 Bad Request: Client sent invalid data.
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication required.
- 404 Not Found: Resource doesn’t exist.
- 500 Internal Server Error: Something went wrong on the server.
Example in Flask
Here’s how you can send different responses:
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
app = Flask(__name__)
# Example GET endpoint
@app.route("/api/hello", methods=["GET"])
def hello_api():
return jsonify({"message": "Hello, API World!"}), 200
# Example POST endpoint
@app.route("/api/user", methods=["POST"])
def create_user():
data = request.get_json()
if not data or "name" not in data:
return jsonify({"error": "Name is required"}), 400
return jsonify({"id": 1, "name": data["name"]}), 201
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
You can use Postman to test your API.
Postman is a widely used, comprehensive API (Application Programming Interface) development and testing platform that allows developers to design, mock, test, document, and monitor APIs. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) to send HTTP/s requests, view server responses, and automate testing, supporting REST, SOAP, and GraphQL protocols.
Download postman from https://www.postman.com/downloads/ and install
How to use postman
See the screenshot below to see how I use Postman to test this API end-points and see the responses I got.
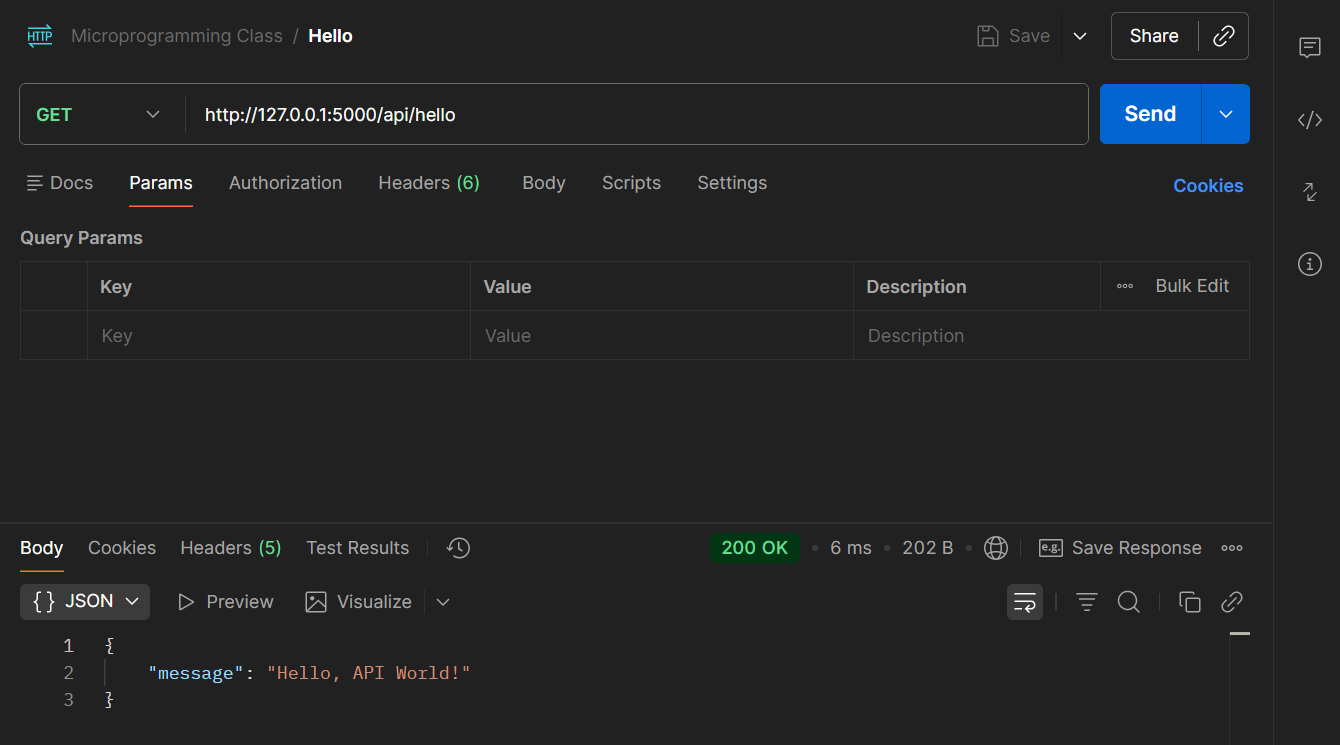
GET /hello endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/hello)
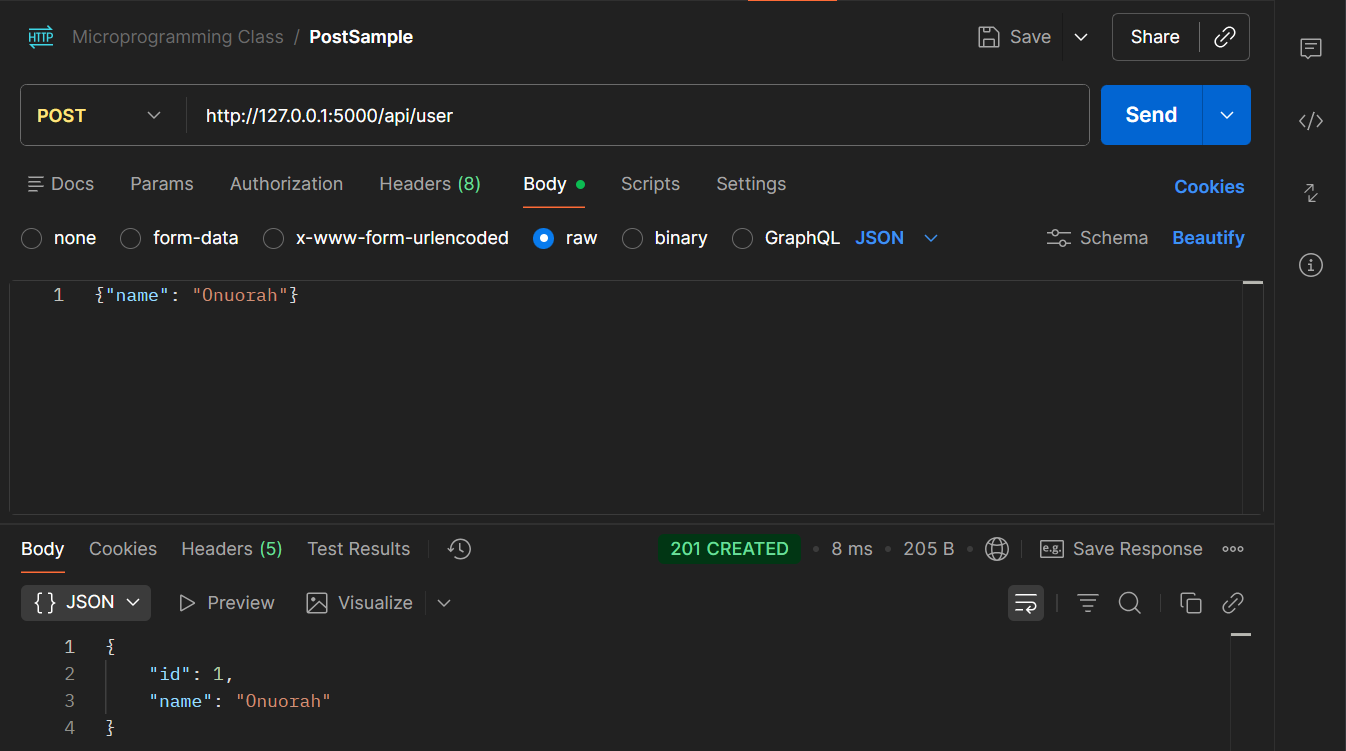
POST/user endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/user) - 201 CREATED
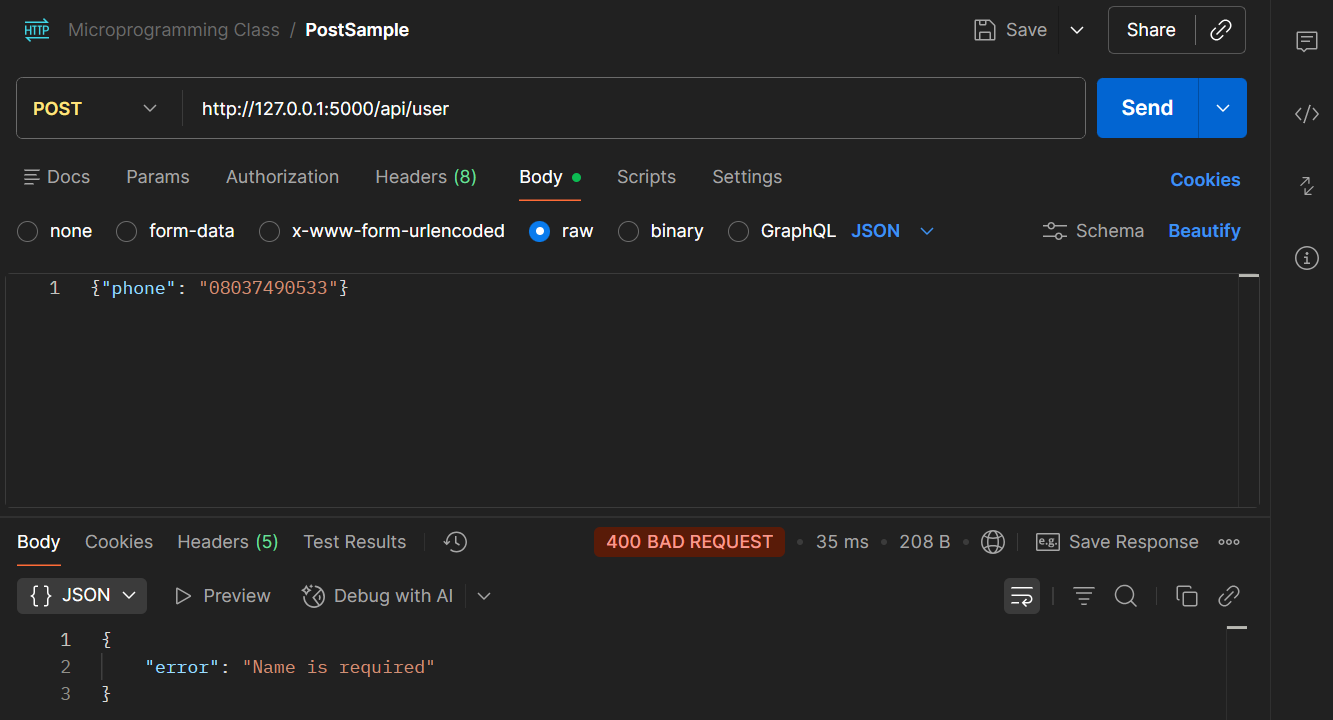
POST/user endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:5000/api/user) - 400 BAD REQUEST
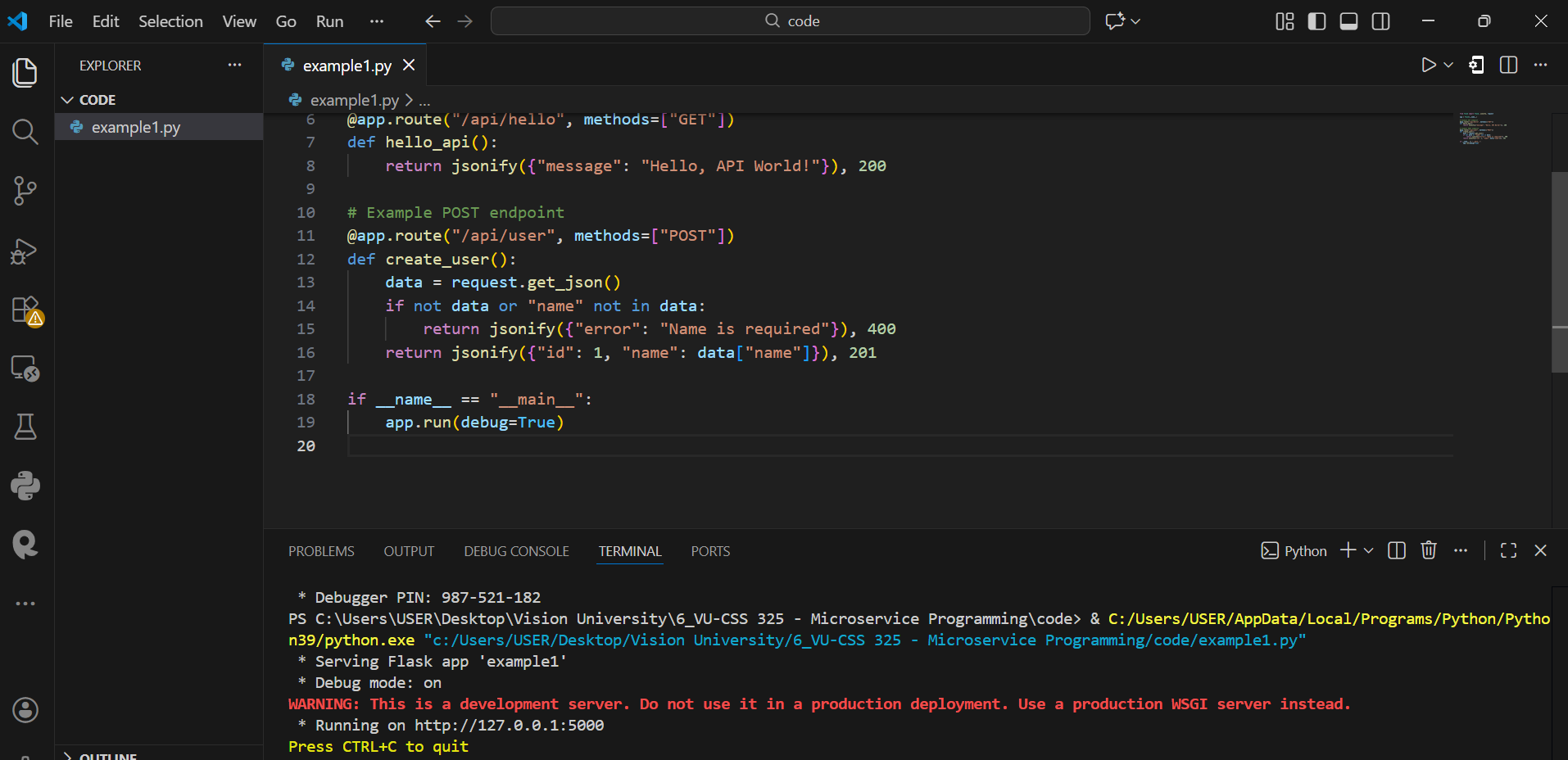
Make sure you run the python code in VS Code and you see the server running
By: Vision University
Comments
No Comment yet!
Login to comment or ask question on this topic
Previous Topic Next Topic